
There is a well-known story on the Internet about a man who, in the early days of Bitcoin, mined a large number of coins and posted an ad offering 10,000 BTC for two pizzas. At today’s rates, that would be an astronomical sum. Back then, however, digital currencies were not taken seriously.
Today, crypto is no longer a novelty. Many users now use digital currencies to generate income and to carry out transactions with others. To process such transactions, intermediaries are needed. These are called crypto processors. In this article, we will take a closer look at who they are and what they do.
To learn more about the different types of cryptocurrencies, as well as other ways of using and earning with digital assets, check out the article “Basics of cryptocurrencies.”
What is processing
Online business is becoming increasingly popular because it is convenient for both buyers and sellers. Buyers do not need to travel to physical stores as they can order goods or services in just a few clicks. Sellers, in turn, save on expenses such as renting premises and hiring retail staff.
Additionally, almost everyone today has a payment card that makes it fast and easy to make purchases anytime and anywhere, even on an airplane. It is convenient because there is no need to carry cash. A single small card is enough, and payments are processed instantly.
Processing refers to the entire set of actions that must be carried out for electronic funds to be transferred from the buyer to the seller. This is performed using specialized software that enables the acceptance, verification, and processing of payments.
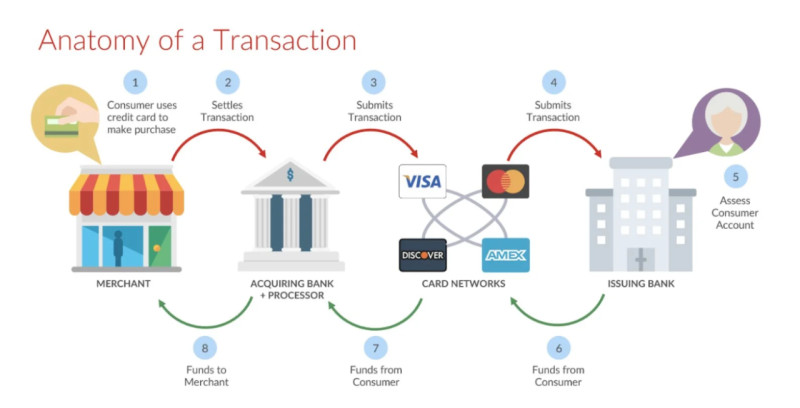
Primarily, this applies to online payments—purchases made in online stores or transactions using bank cards. The verification of all data and the payment process itself are completed within seconds. How is such speed achieved?
To ensure the uninterrupted operation of all these processes, processing centers operate around the clock. These are specialized companies that handle cashless payment transactions. Processing centers connect all the parties involved in a transaction, namely buyers, merchants, and banks.
Participants in the payment procedure:
- The seller, who provides goods or services
- The buyer, who acquires these goods or services
- The issuing bank, which issued the card used by the buyer
- The acquiring bank, which receives the payment from the buyer
- The processing center, which processes the payment
- The payment system, which may be international (Visa, MasterCard) or national (such as "Mir")
Cryptocurrency Processing
With the growing popularity of cryptocurrencies, the demand for conducting transactions with them is also increasing. This applies not only to transferring coins between users but also to paying for goods and services with cryptocurrency.
By analogy with classical payment processing, cryptocurrency processing involves the handling of payments in digital coins. To enable such transactions between businesses offering goods or services and their customers, a mediator is necessary.
A cryptocurrency processor acts as such an intermediary, a company that enables merchants to accept Bitcoin and other digital currencies as payment. The first of these services emerged in 2011. Today, there are dozens of such platforms, and many large, well-known companies are using their services.
So, what exactly do crypto processors offer? Primarily, they handle incoming and outgoing payments for both online and offline services. However, their functions extend beyond that. They may also provide the following supplementary services:
- Custody of crypto assets
- Cryptocurrency exchange
- Brokerage services
- Conversion of crypto into fiat money
- Withdrawal of funds to a bank account or payment system
- Preparation of financial reports
- Technical and legal support
- Compliance consulting
- Data processing and more
Thanks to these intermediary companies, digital currencies are being smoothly integrated into everyday life, and opportunities for using crypto continue to grow. Businesses that accept coins as payment for goods or services benefit from lower transaction fees and increased cash flow.
Below is a comparison table of various payment methods and their key features:
| Payment Method | Fees | Processing Time |
|---|---|---|
| PayPal | 2% (up to $20 for international users) | Funds available on request (with account) |
| Bank Transfer | $40–$65 (for transfers from the US) | 1 business day domestically, 1–3 internationally |
| Cryptocurrency Processing | 1% | From several minutes to several hours |
Cryptocurrency Processing: Key Concepts
Now that we have a clear understanding of what processing entails, it is time to explore how it is implemented in the realm of digital currencies. Two critical concepts must be considered here: the cryptocurrency gateway and acquiring.
A cryptocurrency gateway is a platform that enables the execution of transactions using crypto assets. It is a vital component of the processing infrastructure, responsible for authorizing transactions, encrypting data, and transmitting it securely.
For the end user, the gateway appears as a web page where payment data must be entered to complete a transaction. In the case of fiat payments, this means inputting credit or debit card information. When paying with digital currencies, the user must provide a cryptocurrency wallet address and the transaction hash to confirm the payment.
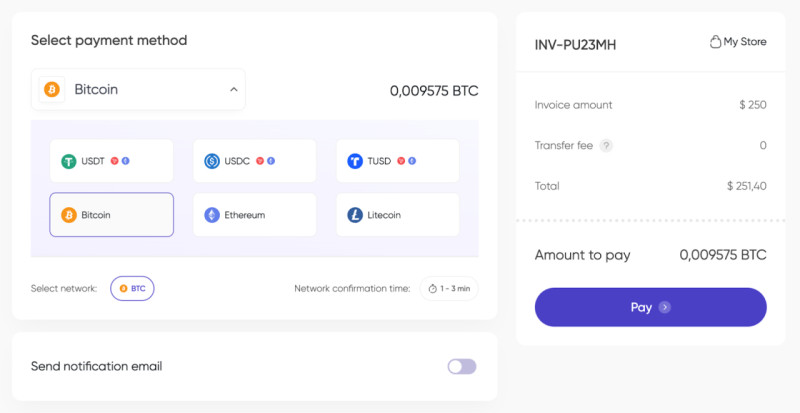
Acquiring allows businesses to accept online payments, including those made in digital coins. It is a specialized service integrated into online platforms to securely receive payments in cryptocurrency.
There are two main types of crypto processors:
- Crypto-to-Fiat
The buyer pays for a good or service in cryptocurrency, while the seller or service provider receives payment in the national fiat currency. The conversion fee is typically around 1% of the transaction amount, and additional currency exchange, banking, and counterparty risk fees may apply due to the involvement of intermediaries.
- Crypto-to-Crypto
The customer pays in digital currency, and the merchant also receives payment in cryptocurrency. In this scenario, the processing service does not rely on traditional banking infrastructure. The average fee is approximately 0.5%, with around 0.1% of that amount allocated to trading costs.
How cryptocurrency processing works
Now that we have clarified the basic concepts, it is time to explore how cryptocurrency processing actually functions. That is, the sequence of steps involved in handling a digital currency transaction. When a payment is made using cryptocurrency, it typically follows these stages:
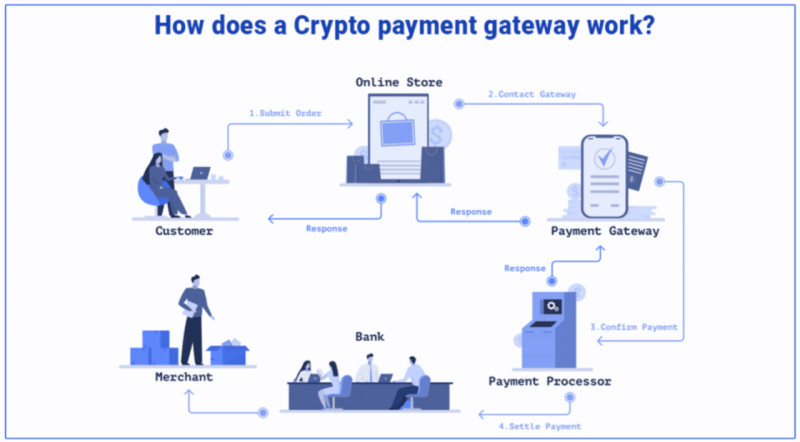
- The buyer selects a product or service on a website, adds it to their cart, proceeds to the checkout page, and chooses cryptocurrency as the preferred payment method.
- The system automatically converts the cost of the selected item into the corresponding cryptocurrency. It then displays the total amount, the wallet address, and a QR code for the transaction.
- After the customer completes the payment, the system sends a request to the blockchain to verify the transaction and check its status. Once confirmed, the buyer gains access to the purchased product or service.
- Upon confirmation, ownership of the transferred funds passes from the buyer to the seller. Depending on the chosen type of processing, the seller receives the payment either in digital currency or in fiat money.
Thanks to blockchain technology, settlements are executed swiftly, securely, and in a decentralized manner. To safeguard data and maintain security, encryption (cryptography) and other protocols are used. Additionally, using cryptocurrency for transactions can significantly reduce fees compared to traditional bank transfers.
At the same time, there are a few characteristics of digital currencies that complicate the payment process. The most prominent is high volatility, making it nearly impossible to buy and sell a coin at the same price.
As a result, a seller may receive a lower amount for a product if the value of the cryptocurrency fluctuates during the transaction. Furthermore, many cryptocurrency networks still lag behind major international payment systems in processing speed. For example, the Ethereum blockchain can handle around 30 transactions per second, whereas Visa can process up to 24,000.
Legal aspects
Conducting transactions using digital currencies presents another major challenge. In many countries, cryptocurrencies are still not recognized as legal tender. As a result, sellers may face concerns about the legalization of such income, tax obligations, and related regulatory requirements.
This legal ambiguity is one reason why many companies are hesitant to accept digital currencies as a form of payment, even though doing so could attract new customers and enhance their reputation as innovative, forward-thinking businesses.
As for the operation of cryptocurrency processors, the intermediaries in this field, the legal interpretation of their activities varies significantly from one country to another. Below, there are a few examples from different jurisdictions.

Under US law, processing activities are equated with banking operations. As such, these companies are subject to banking secrecy laws, anti-money laundering (AML) regulations, and counter-terrorism financing (CTF) measures. Additionally, since 2017, all cryptocurrency transactions have been taxable.
In Switzerland, companies accepting digital currencies as payment are not required to obtain a special license. However, crypto processors are still subject to AML laws and customer identification requirements. Importantly, the activities of intermediary companies are not subject to value-added tax (VAT).
In Estonia, digital currencies are considered legal tender. Crypto processors fall into one of several categories: exchangers, trading platforms, brokers, or alternative payment service providers. These entities must obtain a specific license and register with the appropriate registry. Operations involving cryptocurrencies are exempt from VAT.
Another legal concern arises from consumer protection laws, which generally allow customers to return goods within a specified period and require sellers to refund the payment. However, all cryptocurrency transactions are irreversible, making it impossible for crypto processors to return funds once a payment has been completed.
Future of cryptocurrency processing
Before discussing what lies ahead for cryptocurrency processing, let us take a brief look back at how it all began. The first service to offer such functionality emerged in 2011. It was BitPay.
Following its launch, BitPay quickly gained traction. The company managed to attract a significant number of clients worldwide, and within just two years, it was operating in 164 countries. Later, BitPay secured funding from major corporations such as Virgin Group and Yahoo, which invested $30 million in the project's development.
Starting in 2017, as cryptocurrencies gained more recognition in mainstream markets, a wave of new companies began entering the space to offer crypto processing services. The number of cryptocurrency transactions continued to grow, driving higher demand for transaction processing and increasing the number of intermediary firms, now numbering several dozen.
Competition in this field is intensifying due to the steadily rising volume of digital currency transactions. According to the latest forecasts, the volume of digital currency payments in the real economy is expected to reach between $316 billion and $362 billion by 2026.
As a result, the number of payment systems and crypto processors is expected to grow further, encouraging more merchants and contractors to accept cryptocurrency as a payment method. This will, in turn, contribute to market stabilization and increased liquidity.
However, the key issue that remains central to the development of this sector is legal regulation. Once digital currencies are granted legal tender status in most countries, businesses will be much more inclined to implement crypto payment options broadly across their operations.
How to launch cryptocurrency processing
For most sellers, setting up their own processing center does not make sense, as it is too expensive. Therefore, they turn to third-party companies and implement their ready-made solutions to process cryptocurrency payments.
As a result, establishing a processing center can be a promising business idea. Providing intermediary services in this field involves developing a service platform, converting the cost of goods and services from fiat to cryptocurrency and back, adding new digital currencies, supporting users, and much more.
When launching such a service, it is necessary to consider several important aspects:
- Develop a client acquisition strategy and define the target region. It is essential to understand in which countries cryptocurrencies and operations with them are legal, as well as to consider the specifics of conducting business in this sector within the chosen country.
- Determine the processing model: “crypto-to-fiat” or “crypto-to-crypto.” The features of each of these models have already been discussed above and must be taken into account when choosing.
- Select the cryptocurrency assets for processing. Priority should be given to the most liquid digital coins. It is also important to pay attention to the reliability and throughput capacity of the blockchain in which these currencies circulate.
- Assemble a team of specialists from various fields: IT, finance, technical support, sales, marketing, and legal.
- Choose a liquidity provider, which can be an exchange, broker, or liquidity pool.
- Work out the technical aspects of the project. You can either base your platform on existing processing services or develop it from scratch. It is critical to focus on security measures and protecting the system from hacker attacks.
- Choose a jurisdiction for company registration. Ideally, this should be a country with legislation that is favorable toward the use of digital currencies. This will facilitate cooperation with banks and business clients.
- Sign contracts with banks and payment systems. This is necessary for conducting any operations involving fiat money.
- Calculate your expenses, including employee salaries, platform development costs, marketing, office rent, and so on.
- Set commission rates for your services. Keep in mind that you will not retain the full amount of the commission as an intermediary—part of this income will be allocated to the liquidity provider and payment systems.
Most companies still use fiat money as their primary means of payment and continue to rely on fiat in their operations. Therefore, merchants do not always understand the need to use the services of a crypto processor. It is necessary to clearly demonstrate to them the advantages of your service.
Advantages and disadvantages
We have already discussed in detail what cryptocurrency processing is and how it works. Now, let us take a closer look at its advantages and disadvantages.
Among the advantages are the following:
• Lower commission fees. Transaction fees on blockchain networks are significantly lower than in the banking sector. This is due to the fact that bank transfers involve a large number of intermediaries, each of whom wants to receive a portion of the commission;
• No chargebacks. Buyers often return products after purchase and demand a refund. In the case of blockchain operations, transactions are irreversible, meaning that refunds are impossible. This is a clear benefit for sellers;
• Fraud protection. All cryptocurrency operations are encrypted cryptographically, which provides enhanced data security. This reduces the risk of fraud and protects against theft and data breaches;
• Instant settlements. Cryptocurrency transactions are confirmed quickly because the system lacks a large number of intermediaries. In traditional payment methods, several intermediary organizations are involved, each performing a specific function in the transaction process;
• Simple implementation. Cryptocurrency payment systems are relatively easy to integrate thanks to specialized payment gateways and other technologies. Merchants do not need any technical expertise, as processing services are provided by third-party companies.
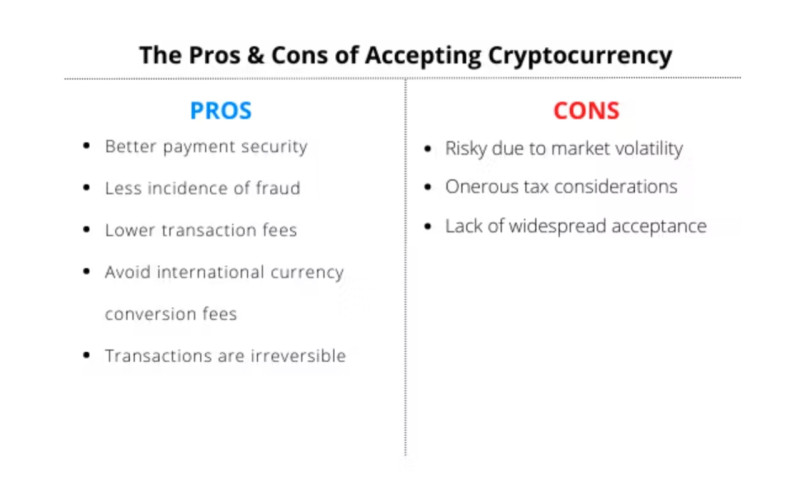
Among the disadvantages of accepting payments in digital currencies are the following:
• Cryptocurrency volatility. Significant fluctuations in the value of digital currencies pose risks, as the exchange rate may change during transaction processing, and the seller may receive less than expected;
• Lack of consumer protection. This is primarily a drawback for buyers: after paying for a product or service in cryptocurrency, it is impossible to cancel the transaction. All digital coin transactions are irreversible;
• Scalability. In many blockchains, the transaction processing speed still lags behind that of major international payment systems. For example, in popular chains like Bitcoin and Ethereum, the speed does not exceed 30 transactions per second, whereas Visa can handle up to 24,000;
• Legal issues. Cryptocurrencies are still not recognized as legal tender in many countries. As a result, merchants may face challenges with legalizing crypto-derived income, tax obligations, and compliance with financial regulations.
Conclusion
In this article, we examined a rapidly growing service, cryptocurrency processing. Its core function is the handling of payments made in digital currencies between buyers and sellers, or service providers. Two main types of crypto processing are available: “crypto-to-crypto” and “crypto-to-fiat.”
In the first case, the buyer pays for a product or service using digital coins, and the seller also receives the payment in cryptocurrency. This model involves fewer intermediaries and lower fees. In the second case, the buyer pays in crypto, but the seller receives the payment in fiat currency. This process involves more intermediaries and higher commissions.
Settlements using cryptocurrencies can be nearly instantaneous. In addition, all data is encrypted, providing protection against criminal attacks. All blockchain operations are irreversible, which means that refunds are not possible. This is a disadvantage for the buyer but an advantage for the seller.
The only limiting factor hindering the development of this area is the legal regulation of digital currency circulation. In many countries, cryptocurrencies are still not recognized as legal tender, and therefore cannot be used for payments everywhere.
However, as digital currencies gain popularity, recognition increases, and laws regulating their circulation are emerging. As a result, cryptocurrency payment processing services are becoming more and more in demand. The creation of your own crypto processor can be considered a promising business idea.
Also read:
Fear & greed index for cryptocurrency
Crypto nodes
Crypto funding rates








 Back to articles
Back to articles



